1.Good safety of gelatin-free.The first lyophilized Varicella Vaccine, containing no gelatin from animals, invented and produced in China. Getting rid of gelatin from varicella vaccine can significantly decrease the ratio of anaphylaxis incidence .
2.Long validity period by good stability. The first approved varicella vaccine with 36 months of validity period in the world. Adopting BH-2 stabilizer with own IP rights (Chinese patent granted No.: ZL200910138411.6, International patent application No.: PCT/CN2009/001405) greatly enhances the stability of the product and ensures the validity period for 36 months under the storage condition.
3.Better protection with high titer and immune eff Varicella Vaccine(Live) Live Bioproducts Pharmaceutical,Live High Potency Medicine,Live Preventive Pharmaceutical,Varicella Biopharmaceutical Live Changchun BCHT Biotechnology Co. , http://www.ccbcht.com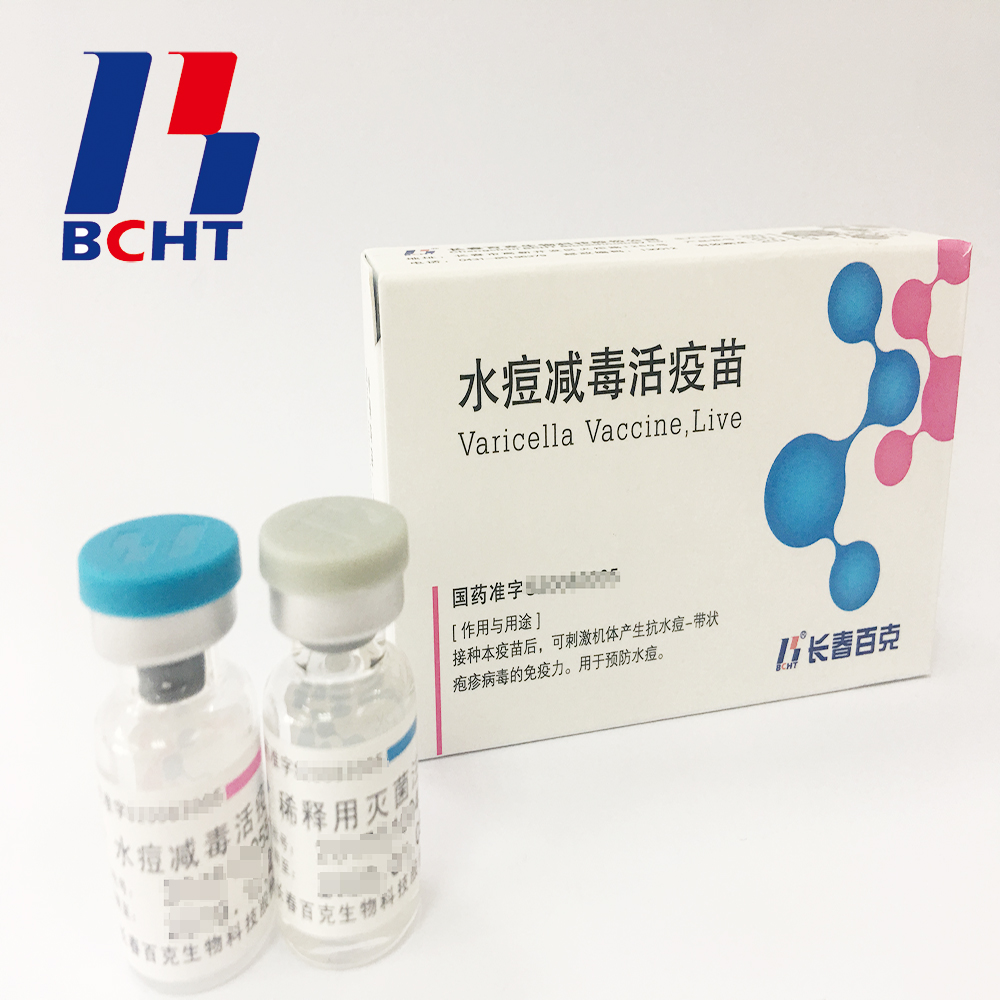 icacy. It`s documented that compared with the varicella vaccine of low titer, high titer vaccine can reduce breakthrough cases by nearly 75% in vaccination. Of all released batches of Varicella Vaccine from BCHT, the titers are not less than 10000 PFU/dose tested by National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.
icacy. It`s documented that compared with the varicella vaccine of low titer, high titer vaccine can reduce breakthrough cases by nearly 75% in vaccination. Of all released batches of Varicella Vaccine from BCHT, the titers are not less than 10000 PFU/dose tested by National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.
Scientists first discovered the control of barley flowering genes
Recently, scientists from the John Innes Center (JIC) in the UK have made breakthrough progress in the study of the crop's best flowering project. The researchers found that a gene known as Ppd-H1 in barley can control the anthesis of barley and is one of the genetic pathways that control barley's response to sunlight. The study will help people understand how to use the length of daylight to ensure that the crops they grow are selected for the best time to bloom. Most plants bloom at specific times each year. Researchers have found that plants have long used the stimulation of the surrounding environment to control flowering. The length of sunshine affects the many crops, including barley, and determines their flowering period. When the sunshine duration in the spring is long, some rapidly responding barley varieties will bloom in early summer, while slower varieties will flower later. In areas where the summer heat is dry, such as in the Mediterranean, early flowering is more advantageous because plants can complete their life cycle before the summer heat. For areas like England that are cool and humid in summer, crops have a longer growing cycle and flowering later, which is more conducive to increasing crop yields. The researchers found that plants, like humans and many other creatures, have an internal biological clock. The circadian clock in barley regulates the activity of the CO (constans) gene, and the peak activity of the CO gene is consistent with the fact that the plant is exposed to long enough light. When the CO gene activates a gene called FT (flowering locus T), it will stimulate flowering, and the Ppd-H1 gene affects the CO gene expression time in a day. Scientists have discovered different genes in late flowering barley. These genes cause the peak of CO expression to be delayed. Therefore, the FT gene can only be expressed when the daytime is long enough, otherwise it will delay flowering. Researchers will further study the different mutations of the Ppd-H1 gene in barley in order to adapt it to different environments. The director of the project, David Lorry, believes that different species of barley or other crops respond differently to the length of sunshine, and the diversity of different species can be adapted to different farming environments. The Ppd-H1 gene, which the researchers identified for the first time to control the flowering response of crops, will help breeders develop new varieties to adapt to changing environmental conditions caused by global climate change. At the same time, the study also helps scientists understand the evolutionary history of crops and helps them understand how crops thrive in different environments around the world.
Next Article
"Two-stage" sheep raising technique
Prev Article
Extrusion processing technology for fish feed (2)