Grapes are native to Europe, West Asia, and North Africa. China has cultivated grapes for more than 2,000 years. The most suitable climate and sunshine: too little sunlight will be sour, too much too sweet. When the vines grow, the temperature is preferably between 20 and 25 degrees. Pollution-free control of common grape diseases First, grape white rot: Harmful fruit, early ear, branch vines and leaves; where the rachis is the most susceptible to infection. The incidence of ear begins with the ear or small fruit near the ground. A pale brown watery lesion appeared in the diseased area. Gradually spread to the ear and fruit. The material and the whole ear are hung on the vine, and it is not easy to fall off. Many grayish white protrusions gradually turn from light brown to dark brown, and the soft rot fruits are easily peeled off. However, there are also shrinkage into a stiff fruit, and there are obvious angular, hanging on the vine, not easy to fall off. When the weather is wet after the rain, black mucus comes out of the spots of diseased fruit. Prevention (1) Chemical control: The key period of prevention and control of this disease is the key protection of the ear during the rainy season from the middle of the flowering season to the mid-August to mid-August. Can be sprayed with 100050% carbendazim, 80050% tumefax or 1:0.5:180 times Bordeaux mixture. Spray once every 10-15 days for a total of 3-4 sprays (add appropriate detergent when spraying to improve efficacy). (2) Physical control, completely cut off the diseased branches, scrape the old skin, remove the diseased fruit, diseased leaves, and diseased vines in time. Eradication of pathogens is also an important measure to reduce the incidence. During the growth period, the lower fruit is tied and suspended to ensure that the ear is more than 20-30 cm from the ground, which can also reduce the incidence. Second, grape black spot disease (black eye disease, scab disease) (I) Symptom recognition Harmful fruit, fruit stems, leaves and shoots. Polygonal lesions appeared after the young leaves were infected, and the veins of the diseased parts stopped growing, causing the leaves to become deformed. When the leaves are affected, a pale yellowish color gradually develops on the main vein and the diseased leaves become dry and perforated. The young fruit suffered brown spots, and after the middle became pale, slightly sag, red or purple on the edges, showing a "bird's-eye shape". The later lesions were cracked and the disease was small and sour. Occurrence of cob sometimes causes whole panicle dysplasia and even dead. (II) Control measures (1) The key to prevention and control of this disease is to seize two drugs before and after flowering. Spray 1: 0.5: 180 times Bordeaux mixture or 80050% Tuzet or 60075% chlorothalonil. Before the germination can also spray 5 degrees sulfur agent. (2) Cut off the diseased vines thoroughly during winter cutting and remove litter. Third, grape downy mildew (I) Symptom recognition The main damage leaves, shoots, young fruit can also be the disease. At the onset of the leaves, translucent water-stained irregular lesions appeared on the front, appearing pale green or yellowish, and the lesions eventually turned yellow-brown or red-brown and dry. Adjacent lesions are connected to a large polygon. At the same time, the grayish-white rhodopes grow on the back of the leaves. After being damaged, young shoots stagnate, twist and even die. When the young fruit is susceptible to disease, white downy mildew occurs on the fruit surface, and growth stops, cracks or falls off. (II) Control measures (1) From the beginning to the beginning of the disease, spray 1:0.5:180 times Bordeaux mixture at intervals of half an hour. Or 100025% of Rhizoctonia or 25040% aluminum phosphate. (2) Remove the litter from the orchard and concentrate it on burning. Fourth, grape anthrax (late rot, bitter rot) (I) Symptom recognition The main hazard is the colored fruit. The ear tip near the ground is the earliest disease. After the fruit was infected, gray and purple patches appeared on the surface, and gradually became a shallow, ringy lesion on the deep edge of the central color. In the future, a small number of black spots are visible in the lesions. With the expansion of the disease, the number of small black spots has continued to increase and they have been arranged in a dorsal pattern. When the air is wet, pink viscous gels are poured from the black spots. The diseased fruit quickly becomes completely soft and rot, eventually becoming a stale fruit and easily falling off. (B) Control methods (1) In July-August, the onset peaked. Once every half month, spray 1:0.5:180 times Bordeaux fluid or 50050% Tuzet (add appropriate detergent to improve efficacy). (2) The disease was discovered before harvesting and timely plucked and buried: After harvesting, the vine was cleared and the disease was buried deeply. Five, nodules (I) Harmfulness and parasite identification The main hazard is the root. After the roots were killed, nodules were produced. At the beginning, it is bright yellow, and afterwards it is rotted in brown, and leaves the leaves of plants on the ground yellow, the fruit is smaller, the tree vigor is weaker, and the yield and quality are significantly reduced. In severe cases, the whole plant can die. The body is soft and looks like a tapeworm, but there is no belly tube in the abdomen. (B) Control methods (1) This worm is one of the important quarantine objects in the international and domestic markets. When purchasing seedlings and cuttings from a suspicious area, it must be strictly disinfected by using 10-20 roots as a bundle and soaking in 150050% phoxim. 1 minute. (2) Remove the diseased plant in time and burn it. Six, two-star leafhopper (small leafhopper, grape two small dust) (I) Harmfulness and parasite identification Harm the leaves. The victim leaves appeared whitish white spots, and later the white spots became white spots. In severe cases, the leaves turned white and fell off, and the ears and branches were not easy to mature. The body is yellowish and 3-3.5 mm long. There are two black round spots on top of the head, yellow-white wings, translucent. The body mostly stays on the back of the leaf to harm. (B) Control methods (1) In the adult or nymph stage, spray 300080% dichlorvos or 150,004% dimethoate or 500020% quick kill. (2) Sweeping orchards in autumn and winter, burning fallen leaves and eliminating overwintering adults. Seven grape red spider (I) Harmfulness Harm the leaves and ears. After the leaves were damaged, many black-brown stripes appeared, and when they were severe, they were scorched off. After the ear was damaged, the spikes were black and became brittle and easily broken. The fruit was rusted after being damaged. Peel rough, sometimes cracking, affecting fruit growth and coloration. (B) Control methods (1) Spray 3 degrees lime sulfur plus 0.3% detergent during spring sprouting. (2) In July-August, 300073% of Ketek or 100040% of dicofol was sprayed. (3) When buried in cold-proof, the old rind of the vine was stripped and burned. Eighty-Star Leaf A (I) Harmfulness and parasite identification Harm the leaves and buds. The leaves were bitten into holes, and all the leaves were eaten when severe, leaving only veins and some membranes. The adults are oval hard-wormed insects, 12 mm long and 8 mm wide. Hard yellow wings, a total of 10 dark spots on the body. Larvae are flat and yellow. Larval larvae often concentrate together when they hatch, and are dispersed when they grow up. Adults often feed on foliar surfaces, but once touched, they secrete a foul-smelling yellow liquid and fall dead. (B) Control methods (1) Spray 120090% trichlorfon or 500020% speed kill. (2) Kill larvae or shake off adults and concentrate on killing. Nine, submerged niches (rust ticks, blanket disease) (i) Harmfulness and parasite identification. Harm the leaves. After the grapes have spread their leaves, white spots appear on the surface of the damaged leaves. Afterwards, the affected part bulges, and the back side is sunken and fluffy. The fluff was gray at first, later became dark brown, and finally brown. The leaves are not flat. Adults are shaped like white kuba. There are four feet at the front of the head. (B) Control methods (1) In the spring, grape buds germinate, and when a few shoots are green, 0.5 degree lime sulfur is sprayed. (2) The branches and branches cut off in winter are concentrated and burned. Ten, grape tiger moth (grape tiger c (I) Harmfulness and parasite identification Harm the leaves. The larvae infested the leaves and severely consumed all the young leaves. The larvae are about 40 mm long after being cooked. The head and tail are yellow, and the back is light green. Each section has large and small black spots with white long hair on it. (B) Control methods (1) In the larval stage, 1200 trichlorfon or 1000520% dichlorvos or 500020% extinction dioxin is sprayed. (2) In the early spring, in the vicinity of the grape roots, excavate the insects in combination with the excavated soil (worm kidney: reddish-brown, 20 mm long, with tails trimmed). The grape points management technology points March Injury period main work: finishing frame, remove cold-proof material Before the grape is unearthed, the loosely hanging wire is tightened and the skewed struts are straightened. At the end of March, the cold-proof soil covered on the grapes will be removed. Care must be taken when removing the soil to avoid touching the shoots. April The main tasks in the budding stage are: putting grapes on top, top-dressing, irrigation, cultivating, eradicating overwintering pests, and wiping buds. Shelves: Grapes unearthed before April 5th. After unearthing, the lichee vines were soft and in the morning, and the main vines were tied to the shelves as far as possible. Attention should be paid to the uniform distribution of the branches when they are tied, and the top is tied to the third wire. The use of flax is recommended. Top dressing, irrigation, cultivator: In early April, the grapes were irrigated before germination, and urea was applied in combination with irrigation soil, and 0.2 kg/plant was applied. Wait until the water is fully infiltrated and the surface is slightly dry, then timely cultivating the soil, and breaking the soil block. Eradication of overwintering pests: When the bud scales begin to expand, spray 3–5 Baume degrees of lime sulfur plus 200 times sodium pentachlorophenol solution to eradicate various germs and overwintering pests. Stubbles: In late April, at the beginning of leaf development, the buds sprouting on old vines were wiped off, resulting in the emergence of branches from the weak branches and secondary buds of the branches. The sprouted litters on the ground were all removed except for the ones used for the update. Early May - Late May The main work: wipe shoots except shoots, irrigated with water, pest control, sparse flower bagging. Twig shoot removal: In early May, wipe off the shoots and shoot the shoots for the second time when the shoots grow to 5–6 cm in length, leaving all the unused branches outside the fruit branches to be wiped out, emphasizing leaving a neat new balance. Tip. When the new shoot grows to about 40 centimeters, the new shoots will be evenly spaced and tied to the frame, and the young part of the new shoot will be removed. Tillage irrigation: In mid-May, irrigation water is poured before flowering, and the water is soaked and weeded. Pest control: spray Bordeaux mixture (copper sulphate 1 kg: quicklime 0.5 kg: water 200-400 kg) before flowering, or 800 times the new high-fat membrane or 400-500 times with 80% dexamethasone to prevent black pox disease. Auxiliary tip treatment: In late May, the minor treatment is performed. Generally, the auxiliary tip below the ear is removed from the base, and the new growth tip is strong. The tip of the 4-5 knots above the ear can also be removed from the base, and then upwards. Auxiliary tip leaves 1-2 leaves topping, 2 tip shoots near the tip of the shoot, leaving 3-4 leaves topping. Sparse flowering: If too many inflorescences are found, some excessive inflorescences may be eliminated. The inflorescences on weak branches may be sparse, and the inflorescences on weaker branches may be sparse from one inflorescence. 3 to 5 days before flowering, 1/4 to 1/5 of the end of the inflorescence was picked off, and the branches and spikes were cut off. Spray 0.2-0.3% borax solution during flowering to increase fruit setting rate. Late May - Late June The main work of the young fruit period: pest control, fruit swelling treatment, top-dressing irrigation, picking tips. Prevention and control of pests: After flowering and fruit setting, spray 1∶0.5:200 Bordeaux mixture 1 time before wheat harvest. Fruit enlargement treatment: 15 days after flowering, according to the instructions, the ear was treated with grape swelling agent. Top dressing irrigation: In mid-June, the young fruit grows rapidly and can be applied with potassium sulfate compound fertilizer (100 kg per mu in full fruit period). After irrigation, the land surface is slightly dry and timely tillage and weeding. Take care of the shoots: In mid-June, take care of the shoots that were kept before flowering. Development branch left 12-15 leaves topping, remove the lower tip from the base, the top 2 secondary tips can leave 2 leaves after repeated topping. When there is little rain and the soil is dry, it should be irrigated and irrigated in time for weeding and weeding. Pest control: In mid-June, 800 times of new high-fat film or 800% of 70% thiophanate-methyl was used to prevent botrytis cinerea, and the bag was timely bagged after spraying (special bag for grape). In late June, spray Bordeaux multi-solution (1:0.5:200), can be added at the same time to remove 2000-3000 times liquid. Mid-July Hard core work: irrigation, spraying, topping Keep the soil moist, timely irrigation, and timely cultivating and weeding, spray Bordeaux fluid (1:0.5:200). Tailoring tips. July - end of August The main tasks of the fruit coloring period: pest control, topping, drainage, picking leaves, fruit harvesting Pest control: In late July, spray 800 times the new high-fat film or Fukmi double 500 times plus 70% 600 600 tons of liquid to prevent white rot. In early August, 500 times the special bacteria used for spraying, 50% carbendazim 600 times + 0.2-0.3% potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution to prevent anthrax. The downy mildew-infested grapevine sprayed with metalaxyl + mancozeb solution was used for prevention and treatment. In late August, if there is no disease, Bordeaux fluid (1:0.5:200) can be used to prevent diseases. Topping: In late July, toppings, preparatory branches, and sprouting twigs must all be picked up, and the auxiliary shoots must be picked up. Drainage: In the rainy season, low-lying vineyards should pay attention to timely drainage. Timely weeding to avoid aggravating pests and diseases. Picking leaves: In late August, the old leaves, which are close to the shade, are removed to increase the degree of fruit coloration. Fruit harvesting: At the end of August, medium-yielding varieties such as Kyoho were harvested. September - October The main work of fruit harvesting period: picking the heart, harvesting the fruit, and applying base fertilizer in autumn. Topping: In September, continue picking up on unstopped shoots. The fruits were harvested in the middle and late September, and the fruits of the late-maturing cultivars were harvested. The weather was selected to be clear and windless. After the dew was dry, it was harvested to facilitate storage and transportation, and the bad grains and diseased grains were cut after harvesting. Autumn basal fertilization: After the fruit is harvested, the basal fertilization is performed. It is ideal to use adequately rotted chicken manure (self-made) for autumn fertilization. A fertilization furrow is to be opened on the same side of the tree body with a depth of 30-40 cm and a width of 30 cm. Decompose chicken manure by 3 m3/mu, potassium sulfate compound fertilizer by 120-150 kg/mu, borax by 20-25 kg/mu. Spread in the ditch, mix thoroughly by deep turning, backfill the topsoil, and apply water after application. Cultivator. November - early December The main work of the deciduous period: pruning in winter, clearing the park, and burying the soil in the cold. Winter pruning: Pruning in winter must be carried out after the vine is completely deciduous and before the soil is frozen. First, the amount of branching should be determined and then trimmed. Determine the amount of left branches: Before the pruning, observe the growth of the whole garden and calculate the stock of the female branches according to the growth of the seedlings. The number of mother trees to be left per acre of land = the required output per acre of vineyard (kg)/(average number of branches per acre, average number of acre per acre, average weight per ear), generally 4000 – 5000 acre Leave the result of the mother branch. Colonization of the saplings in the year of planting: The length of the main vine was cut to bind the length of the vine to the length of the wire, which was determined according to the growth of the tree body and the degree of fullness of the buds. Results Pruning of branches: In the fruit period grapevine pruning, on the branches of the results of the year, two full shoots are cut off and the rest are cut off; the development branches with space can be trimmed as well. The tree's result position moves upwards, and the developmental branches that are sprouted in the lower part of the main vine can be left as a reserve branch, and the resulting branch group is updated. Clear Garden: The diseased branches, dead branches, and cut-off pests and branches of the park were burned and eliminated pathogens. Buried in the cold: the fenced plants can rake along the ditch (40 cm wide and 30 cm deep) and place the bundled plants in the ditch. The plants are buried about 30 centimeters in depth. To ensure safety, they can be planted on plants. A layer of straw is covered first, and then the soil is buried on the covering. Early December - February The main work during the dormant period: composting and fattening, formulating vineyard work management plans for the whole year, preparation of frame materials, pesticides, and fertilizers. If the vineyards are initially built, the stands can be prepared (mainly iron wires and cement columns), and the preparation of pesticides is mainly preparation of lime sulfur. Attachment: Construction and structural specifications of the fence The direction of the fence is north and south, and the spacing is based on the planned shed distance. The height is 1.8-2 meters and the column distance is 8 meters. The middle column is 8 centimeters and 12 centimeters thick and 2.4 to 2.5 meters high. Columns with four 6.5 mm diameter steel bars, buried depth of 0.5-0.6 meters, side column specifications: 12 cm thick 12 cm, 2.5-2.8 meters high. The depth of buried soil is 0.6-0.8 meters, and the slope is outward 20o-30o. The 8th iron wire is fixed and tightened with anchor stone. Each column wears 4 No. 10 iron wire, the first layer of iron wire is 0.4 meters away from the ground, and the spacing of each wire is 0.4 meters. Grape Easy Storage First, pre-storage treatment (a) Pre-harvest spraying. Full flower spray 110-6 concentration of gibberellic acid plus 1000 times liquid chlormequat, 20 days before fruit picking, spray 1500 times liquid thiophanate-methyl, 3 to 5 days before harvest, spray 10000 times liquid naphthalene acetic acid to prevent cracking , fruit drop, increase fruit coloring, increase sugar and prevent the occurrence of spores, head blight and white rot. (b) Fruit harvesting. Choose late-maturing red earth, black mention, black lotus seeds, black Olin, Dabao, Kyoho and other varieties. The fruit should be fully matured, with good color, fruit powder, thick skin, strong toughness, high sugar content, strong fragrant taste, and storage resistance. To dry after dew harvesting. Harvesting and storage should be done gently so as not to break the fruit and wipe off the fruit powder. (C) cooling pre-cooling. Collect the ears, remove the damaged fruits and pests and fruits, repair the irregular spikelets and deputy ears, and apply the melted wax to cut the cut stems and spread them on a straw mat in a cool, well-ventilated and cool room. 2 to 3 days after the heat is stored before cooling. Second, the storage method (a) cold storage. In the bottom of the box and around the lining of 3 to 4 layers of soft paper, put 0.04 ~ 0.06 mm thick film pressed into a storage bag, fitted with pre-cooled ear, 10 kg to 15 kg per bag, Put a piece of sulphur dioxide preservative into the bag, seal the bag mouth, and then store the box number in the library. Can also be erected in the vertical column inside the store, every 30 cm on the rack to wear a mattress, smashed on the bamboo or straw mats, the bunch of fruit on the curtain, put a layer of each layer in order to avoid pressure injury Fruit grains. (B) storage in the cellar. The cellar building is the same as the apple cellar. The cellar is cleaned first and sprayed with 1000 times liquid to disinfect. Place a bamboo stick every 12 to 15 centimeters on the fruit box, twist the bunch of fruit on the stick, and then move it into the pit of the cellar. It is advisable to use 3 layers high and seal the pit. Can also be set up on both sides of the cellar vertical column scaffolding, stratified layering, spacing 30 to 35 cm, 15 to 20 cm in diameter, the ear hanging on the lotus root, ear spacing 4 to 5 cm, with 4 layers is appropriate . (c) film bags storage. Using a 0.04-0.06 mm thick polyethylene film, press and grow 40 cm. A 30-cm-wide sachet, each containing 1.5kg to 2kg of fruit, is tied over the mouth of the bag, and put on a pad of 4 to 5cm thick sawdust or smashed straw in the bottom of the person's bottom. Only one layer of fruit is placed in each box. , Place the box in a cool room or in a storage room. Check wooden box can be moved, but can not open the bag, even if there are 1 or 2 pieces of fruit and mildew, do not open the bag, once opened, the bag of oxygen suddenly increased, it is difficult to continue the container. (d) tile storage. Use a tile cylinder 70 cm high and 60 to 70 cm in waist diameter. After washing, dry the cylinder mouth downwards. Put a clean soft tissue on the bottom 3 layers, put 2 to 3 layers of the ear, about 25 cm thick, and put it into the well. The glyph wooden frame is stuck in the waist of the cylinder, and the frame is covered with a film or soft paper, and a hole of 1 cm in size must be punched every 8 to 10 cm square to facilitate ventilation. The ear of fruit should be placed on 1 to 2 layers. 15 to 20 centimeters, put the cylinder into a cool room, not sealed in the early stage, and seal it with a paper seal 1 month later. After the weather has warmed, the ventilation openings and window doors are closed during the day and opened at night to reduce the room temperature and can be stored until the following Spring Festival. After the cylinder is opened, it must be processed once, and it is absolutely impossible to seal the cylinder again, so as to avoid deterioration of the oxygen in the cylinder. Third, post-storage management (a) Regular inspections. Check once every 15 to 20 days, adjust the temperature and humidity, so that the temperature and humidity are maintained within 0 to 3 °C and 85% to 90%, too high or too low, too dry or too wet, are not conducive to storage. (2) Burning sulfur and antisepsis. In the storage room (room), the storage capacity of 20 grams of sulfur per cubic meter, sulfur burning once every 10 days, bactericidal anti-corrosion. (China Plant Protection Network: Li Ruifeng)
We totally take the advantages of foreign feed mixers, simple operation, easy maintenance and practical. The lubricant refueling points is located in the outside.
Animal Feed Mixer,Tractional Tmr Feeding Mixer,Traction Feeding Mixer,Traction Feeding Mixer Machine Henan Leo Husbandry Equipment Science and Technology Co.ltd , https://www.chinaleodairy.com

Annual Annunciation Management Technology
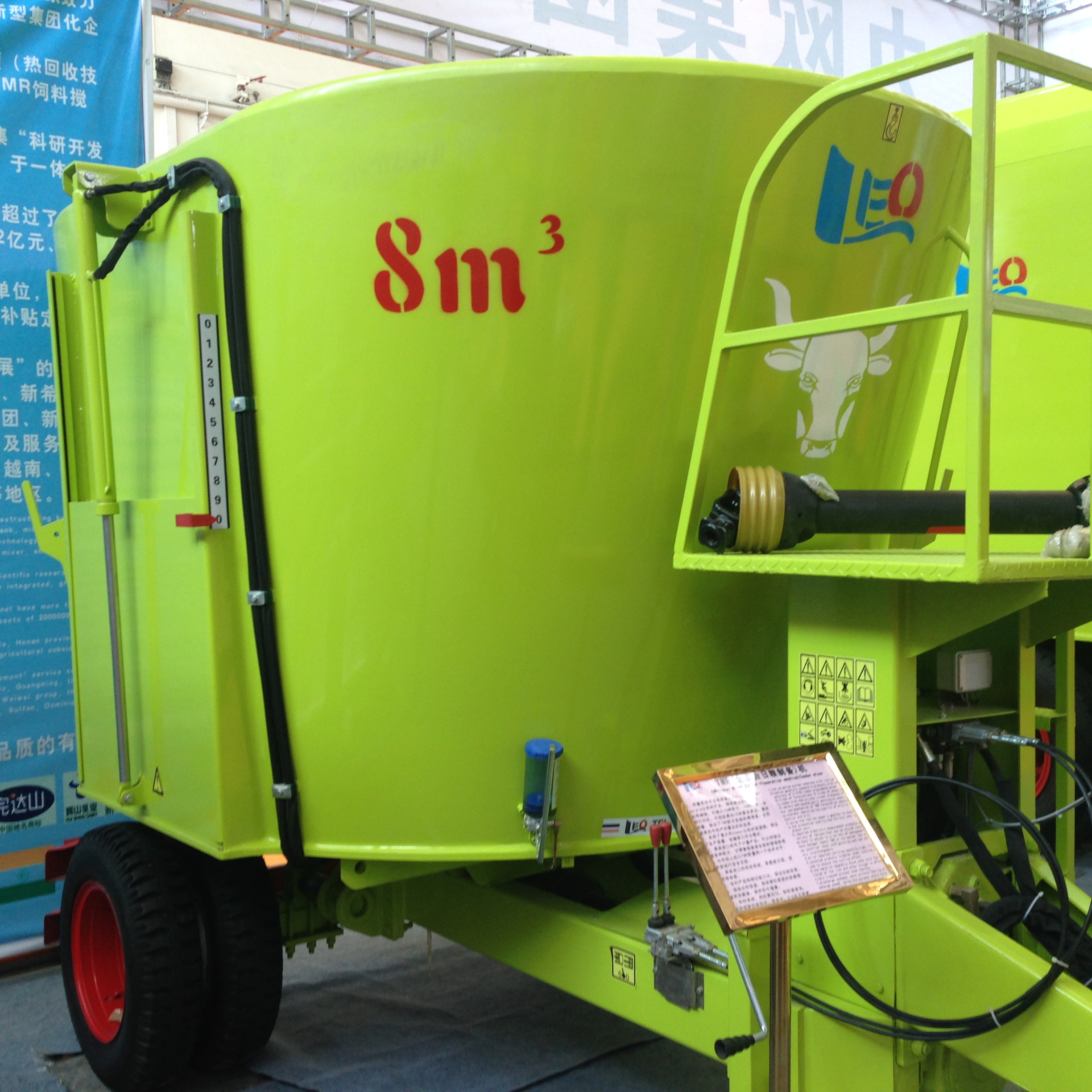
LEO seriesTMR Feeder Mixer / Vertical Mixer Wagons/fodder mixer Features:
1.Introduced the Italian original parts and assembly line to produce our LEO Series TMR Feed Mixer equipment
2. There are vertical fixed type, vertical traction type, horizontal fixed type, horizontal traction type, vertical self-propelled type and so on;
The capacity from 5 cubic meters to 42 cubic volume.
Thicken high wear resistant manganese box
The material thickness of feed mixer main body is above 8mm, bottom is above 15mm.
Ensure the life of the machine is 1.5 times than others.
Mixing tank is made by a high-quality16Mn alloy steel plate , better wear resistant and longer life. The special angel tilt design of mixing tank sidewall can resolve the pressure from materials to sidewall also can greatly improve the anti-wear of mixing tank .
Next Article
June Ginger Cultivation Technology
Prev Article
46 safe driving skills to pay attention