[ Abstract] LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System) is a comprehensive management of sample inspection process, analysis data and reports, laboratory resources and customer information, and establishes conformity according to standardized laboratory management regulations. The quality system of the laboratory business process, to achieve laboratory information management. It is an information platform for the laboratory to improve the level of analysis, standardize the sample testing process and reduce the cost of the experiment to provide excellent service to customers. LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System) is a laboratory information management system that establishes laboratory compliance with standardized laboratory management practices through comprehensive management of sample inspection processes, analytical data and reports, laboratory resources, and customer information. The quality system of the process realizes the information management of the laboratory. It is an information platform for the laboratory to improve the level of analysis, standardize the sample testing process and reduce the cost of the experiment to provide excellent service to customers. This article introduces some of the basic functions of the LIMS system. Testing application The test application is the first step of the LIMS business management process. The test application is usually submitted by the customer directly through the LIMS or the laboratory related service department assists the customer or replaces the customer to fill out the test application. LIMS should record information about the application test customer (internal or external), information about the test sample, test requirements and special requirements. The customer filling out the test application must be an authorized customer in the LIMS. The system can also record the information filled in, the person to fill in, the time to fill in, and so on. And should support the export and print paper application form. The advanced LIMS can provide a variety of application form entry methods, such as information import, fill in test applications via the Internet, and directly send inspection tasks from other business information systems. Contract review and sample receipt After receiving the customer test application and samples, the relevant personnel of the laboratory will review the application in the LIMS and check whether the sample submitted is deviated from the application. Detect task assignment and assignment The LIMS should be automatically assigned to the inspector or inspection group by identifying the inspection department associated with the inspection task and the authorization status of the test. For special users, it is also possible to assign inspection tasks by means of manual deployment. Test result entry The entry of the test result refers to the process of inputting the test result into the LIMS in various ways after the sample test is completed. The entry of test results is an important part of LIMS. Advanced LIMS provides a number of useful features to assist inspectors in the testing and entry of results and for better quality control. Automatic calculation The test method is programmed into the LIMS, and the tester can complete the calculation of the final result by inputting the test result of the instrument. Instrument data acquisition Through automatic acquisition, the results of the instrument output, test spectra and other results and original records are directly imported into the LIMS, reducing the workload of the tester and reducing possible errors. Results and original record collection in multiple formats A large number of non-data result files, such as photos, images, experimental spectra, etc., can be saved by LIMS. Correction of results by quality control samples Many LIMS introduce the concept of test batches, using the same instrument, the same test method, and many samples in a batch, for example, a content determination experiment with an ICP with automatic injection function. The tester can add quality control samples to each batch and correct the results of the batch samples according to the test results of the quality control samples. For example, if the test results of the quality control samples exceed the specified range, the results of the whole batch of samples are invalid. The instrument calibration needs to be re-executed and the test repeated. View detection methods and SOPs LIMS can be associated with the corresponding operating instructions, instrument instructions, and test method files. During the testing process, the inspectors can easily query the currently valid versions of these related technical documents. Test workflow If the laboratory performs some of the tests, it will take many people and complete the steps. For example, a test requires multiple steps such as sample preparation, weighing, digestion, constant volume and on-machine experiment. These steps may be completed by different inspectors. For such cases, the definition of the test workflow can be defined by LIMS. The time of the operation, the operator and other information. Data modification tracking A complete LIMS should have a data modification tracking function. For the entered and modified detection data, the system should record the entry or modification of the person and record the time when the operation occurred for traceability. Data and report review Data and report auditors conduct audits of test data and test reports through LIMS. A good LIMS should have the ability to report auto-generated. Data and report auditors should be able to view and review test results data, as well as relevant quality information during the test, such as instruments, standards, and test personnel used in the test. The review of data and test results reports requires verification by electronic means such as electronic signatures to ensure that the operator is legally authorized. Sample management Sample management is a very important part of LIMS. The LIMS should dynamically record the entire process from the arrival of the laboratory to the end of the test until the user retrieves the sample or is disposed of by the laboratory. When the sample enters the laboratory, the user can record in the system the time the sample arrived, the current state of the sample, and whether it deviated from the described or specified conditions. LIMS should identify the sample by means of bar code, etc., and ensure the uniqueness of the sample identification to facilitate the transmission and query of the sample throughout the inspection process. LIMS should provide information on the location and conditions of the sample storage. If possible, the storage location that meets the storage conditions should be automatically assigned by identifying characteristics such as sample properties and materials. The retrieval and return of the experimental samples should be recorded in the LIMS, and the retrieval and return operations can be performed by means of barcode scanning. For samples that need to be disposed of beyond the date of sample retention, information such as the method of disposal and date of disposal should be recorded in the system. Subcontract management LIMS needs to effectively control and manage this work when the laboratory needs to subcontract the inspection for unforeseen reasons or for continuous reasons. First of all, in addition to the specific subcontractor designated by the customer, the testing organization or laboratory subcontracted by the laboratory must be a laboratory that has been evaluated and approved by the laboratory. Information on the subcontracted laboratories needs to be maintained in the LIMS, including information on its testing capabilities, quality system status, relevant qualification certificates, and contact information. LIMS can also save electronic versions of subcontracting agreements, subcontractor audit records, etc., if needed. When LIMS subcontracts samples, it should be able to output subcontracting requisitions. When outputting information, the principle of customer information should be ensured. LIMS should provide tracking functions for subcontracted samples, including subcontracting dates, such as mailing samples, and tracking samples by courier number. After the test report is issued by the laboratory performing the test task, the laboratory can input the result of the subcontract into the LIMS. If necessary, the report scan or electronic version issued by the laboratory performing the test task can be stored in the system. Personnel management The personnel management in LIMS is not as large and complete as the human resources system. Although it contains some basic information of personnel, the personnel management in LIMS should be more focused on the management of personnel's detection ability, training and authorization. LIMS should be able to maintain relevant technical files, educational background, qualifications, current job descriptions and other relevant information. The personnel training process is a dynamic process that includes training plans, training implementation and training assessments. The laboratory can select training programs that are compatible with current and expected testing tasks through LIMS, and evaluate and revise the plans based on actual conditions. The laboratory can notify the trainers through the LIMS notification and distribute the training-related electronic materials and materials through the system. Participants can also use feedback from LIMS to improve the relevance and effectiveness of the training. LIMS should also provide relevant training functions such as training assessment and training materials. LIMS should maintain the authorization of personnel and control the process according to these authorizations. If the authorized signatory is not authorized by the system, it is not allowed to issue a test report. An inspector cannot perform the experiment without the authorization of a test method and instrument. Instrument and meter management The management of instruments and test instruments in LIMS is also different from our common fixed asset management system. It is divided into static data management and dynamic management. The static management of the instrument includes the management of basic information of instruments and equipment, the management of instrument accessories, and the maintenance of instrument technical parameters. The dynamic management of the instrument includes periodic inspection of the instrument, routine maintenance, calibration of the instrument, verification of the instrument, traceability of the source, and management of the instrument status. Through the dynamic management of measuring instruments, laboratory inspectors and managers can keep track of the condition of the instrument and ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the test results. Reagents, reference materials and supplier management The procurement process for reagents and reference materials is usually not managed in LIMS. However, suppliers who supply these reagents and reference materials need to be managed. Information on qualified suppliers approved by the laboratory, such as address, contact information, catalogue of supplied reagents and reference materials, etc., needs to be maintained in the LIMS. For each batch of reagents purchased, their suppliers should be recorded for traceability. LIMS should also manage the storage and inventory of reagents. For reagents and reference materials that seriously affect the test results, LIMS should record the reagent lot number used in each test or record by barcode scanning. Method management LIMS should perform strict version control of the experimental method, and ensure that the detection methods used by the laboratory are consistent and currently valid through the version update and control of the method in the LIMS. Facility and environmental condition management With the continuous development of science and technology, more and more laboratories use thermometers and hygrometers that can perform data acquisition and analysis, and instruments for measuring electromagnetic interference, radiation, and vibration levels in test environments. Through the combination of LIMS and instruments in these real-time monitoring laboratory environments, it is possible to more effectively monitor and analyze the environmental conditions of the laboratory, and to correlate environmental conditions with instruments and test items, and set environmental condition thresholds when the corresponding threshold is exceeded. , reminders and warnings to testers through LIMS. Ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the test results. Document management LIMS should also manage the laboratory's technical documents, quality documents, inspection standards, calibration specifications, and other related documents to achieve the management and monitoring of the drafting, release, modification, and review of the entire process. Establish a file directory and classification to control the file level. The file can be freely queried, that is, by specifying any query condition for querying or fuzzy query, and printing the obtained file. Files can be added and deleted for deletion (discontinued) files. Marked, and there are notes explaining the reason for deletion, and the file issuance can be recorded. When the file is nearing invalidity or exceeds the validity period, the system automatically reminds the file administrator to handle it accordingly. Laboratory quality control Laboratory quality control is the control measures taken to control the error of the analytical test results within the allowable limits. Traditionally, we conduct quality control of laboratories through in-lab quality control and interlaboratory comparisons. In the laboratory, quality control generally includes blank experiments, calibration of calibration curves, calibration of instruments and equipment, analysis of parallel samples, analysis of standard samples, and use of quality control charts. The inter-laboratory comparison includes the evaluation of the analysis results of the laboratories by distributing the standard samples, the collaborative experiment verification of the analytical methods, and the examination of the cryptographic samples. It is an important measure to detect and eliminate systematic errors between laboratories. Laboratory quality control can be performed via LIMS. LIMS's management of quality control is reflected in two aspects. First, there are planned, purposeful and targeted treatment of the test samples and comparison tests and evaluations between the laboratory and the laboratory. Another aspect is the processing of quality control samples in the daily inspection work, the calibration curve of the test instrument, the trend graph of the test results and the control chart. Laboratory quality activity management The daily quality activities of the laboratory can be managed through LIMS. For example, management review, internal review, corrective actions, preventive measures, non-compliance with inspection work control, etc. These quality activities can be managed dynamically through LIMS, or through other office automation systems for process management or paper flow management. However, as mentioned in the article above, the essence of LIMS is actually the materialization of laboratory management ideas. Therefore, the continuous improvement measures and management process adjustment requirements proposed by the laboratory through quality activities are reflected on the LIMS, and are constantly improved. Serve the management system. Customer service Customer performance through LIMS service is on two levels. The first is to protect the privacy of customer information more effectively through information management. The second is to provide customers with better services through LIMS and its related extension functions, such as establishing customer feedback and complaint platform, downloading test reports directly through the Internet, verifying the authenticity of the report online, and inquiring the progress of the test through the Internet at any time. Send SMS or email reminders to authorize customers to submit test requests directly via the Internet. Result report management A very important function of LIMS is to automatically generate test results reports, and many laboratories now use this feature of LIMS first. It is usually implemented by using a third-party reporting tool or a self-developed reporting tool to set a report template in a certain format, and automatically obtain the test result data and the information required by the customer to explain the detection or calibration results and the method requirements. Automatic organization and report generation. No manual intervention is required during the generation of the report. The template for the report should be developed in accordance with laboratory requirements and the Requirements for Accreditation of Test and Calibration Laboratories to ensure that the necessary information is provided. The information in all reports must be extracted from the system database. In other words, any customer information, test and method information, instrument information, and experimental result information embodied in the results report must be identical to the information in the LIMS database, and This information can be traced back in the system. If the LIMS provides the function of electronic transmission of results, when the result report is sent by WEB mode or automatically sending mail or electronic facsimile platform, the system needs to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the result report in the transmission process. Eliminate the risk of transmission and protect customer information. Data statistics and queries The biggest advantage of an information system is the ability to count, query, and analyze data. Through the establishment of LIMS, laboratory managers no longer need to judge through experience, but through more scientific and accurate large-scale statistical data management decisions and management systems and quality system improvements. Thus, a statistical and query function of LIMS is a very important function. A good LIMS should have open, powerful, and customizable query and statistics capabilities. Content from web data
Intermediates of Cladribine, Carvedilol, Lurasidone, olmesartan,
Risedronate Sodium, Atazanavir, Saxagliptin,
Dabigatran,Dapoxetine,Cefixime,Ceftaroline fosamil and etc.
In the short span of time, we have emerged as most promising
pharmaceutical intermediates manufacturers, chemical intermediates and
bulk drug intermediates suppliers. Our consistent supply, quality
products and dedication towards clients have opened up many
international avenues for our growth.
In addition, the company also can follow the customer's product needs custom synthesis services
MAIN API PRODUCTS USP/BP
PRODUCT NAME
CAS NUMBER
SPEVIFICATION
Azithromycin
117772-70-0
BEP
Cefpirome Sulphate sterile
84957-29-9
USP JP16
Ceftriaxone Sodium (Sterile)
104376-79-6
USP31
Cefotaxime
64485-93-4
USP30
Ciprofloxacin HCL
85721-33-1
USP/BP
Gentamicin sulphate
1405-41-0
BP
Levofloxacin
100986-85-4
USP27
Lincomycin Hydrochloride
859-18-7
EP6.0
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride
186826-86-8
USP31
Tigecycline
220620-09-7
USP
Linezolid
165800-03-3
EP
Dexamethasone
50-02-2
USP/BP/EP
Methylprednisolone
83-43-2
USP/BP/EP
Dexketoprofen trometamol
156604-79-4
BP2008
Ibuprofen
15687-27-1
BP
Metamizol
68-89-3
DAB
Sulindac
38194-50-2
USP/BP/EP
Naproxcinod
163133-43-5
USP28
Tripelennamine Hydrochloride
154-69-8
USP28
Itraconazole
84625-61-6
USP/BP
Cytarabine
147-94-4
USP31
Leucovorin Calcium
1492-18-8
USP32
Valsartan
137862-53-4
USP30
Telmisartan
144701-48-4
USP31
Rosuvastatin Calcium
147098-20-2
USP/BP
Pitavastatin Calcium
147526-32-7
USP/BP
Fluvastatin
93957-54-1
USP31
Vinpocetine
42971-09-5
EP6.0
Atazanavir
198904-31-3
BP
Rosiglitazone
122320-73-4
USP30
Esomeprazole Magnesium
161973-10-0
USP/BP
Topiramate
97240-79-4
USP31
Fexofenadine HCl
153439-40-8
Inhouse
Bosentan
147536-97-8
Inhouse
D-Cysteine
921-01-7
Inhouse
D-Phenylalanine
673-06-3
Inhouse
Linagliptin
668270-12-0
Inhouse
Rivaroxaban
366789-02-8
USP
Saxagliptin
361442-04-8
USP
Vildagliptin
274901-16-5
USP
Major Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Mica Ester,Pharma Intermediates,Ciprofloxacin Hcl Uses,Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients NINGBO VOICE BIOCHEMIC CO. LTD , https://www.medicine-voice.com
Items Descripation
Structure
Application
MICA ESTER
CAS No: 246035-38-1
Purity: ≥98%
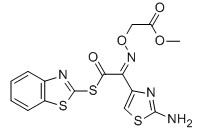
For Cefixime
EHATA
CAS No: 64485-82-1
Purity: ≥98%
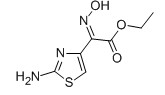
For Ceftazidine
2-Chloroadenine
CAS No: 1839-18-5
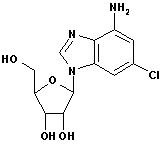
For Cladribine, Fludarabine et al
Bicyclo(2,2,1)Heptane-2,3-di-exo-carboximide
CAS No: 14805o-29-9
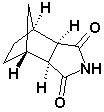
For Lurasidne
(R,R)-1,2-Bis(methanesulfonyloxy methyl)Cyclohexane
CAS No: 186204-35-3
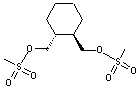
For Lurasidone
3-(Piperazin-1-yl)benzol[d] isothiazole
CAS No: 87691-87-0
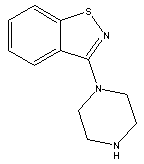
For Lurasidone
Trityl olmesartan
CAS No: 144690-92-6
Purity: ≥98%
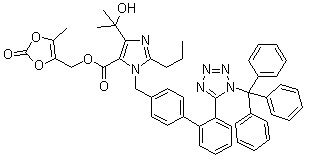
For olmesartan
3-Acetyl Pyridine
CAS No: 350-03-8
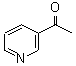
For Risedronate Sodium
3-(AceticAcid)pyridine HCL
CAS No: 6419-36-9
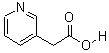
For Risedronate Sodium
Risedronic Acid
CAS No: 105462-24-6
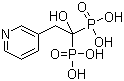
For Risedronate Sodium
3-Hydroxy-1-adamantyl-D-Glycine
CAS No: 709031-29-8
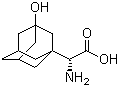
For Saxagliptin
(1s,3s,5s)-3-(aminocarbonyl)-2-azabicyclo(3,1,0) hexane-2-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
CAS No: 361440-67-7
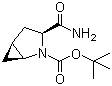
For Saxagliptin
(S)-N-Boc-3- hydroxy-adamantylglycine
CAS No: 361442-00-4
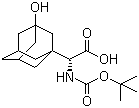
For Saxagliptin
2-Azabicyclo[3.1.0] hexane-3-carbonitrile, (1s,3s,5s)-
CAS No: 866083-42-3
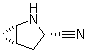
For Saxagliptin
Ethyl 3-(pyridin-2-ylamino) propanoate
CAS No: 103041-38-9
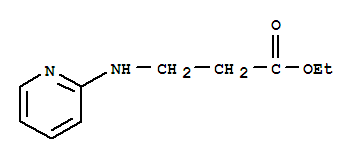
For Dabigatran
N-(4-Cyanophenyl) glycine
CAS No: 42288-26-6
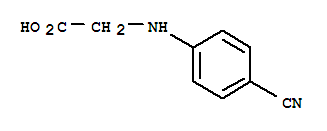
For Dabigatran
4-methylamino-3-nitrobenzoic Acid
CAS No: 41263-74-5
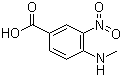
For Dabigatran
S-3-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid ethyl ester HCL
CAS No: 167834-24-4
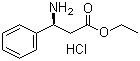
For Dapoxetine
(S)-3-Amino-3-Phemylpropan -1-ol
CAS No: 82769-76-4
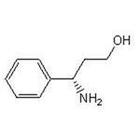
For Dapoxetine
(S)-3-Dimethylamino-3-Phemylpropanol
CAS No: 82769-75-3
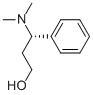
For Dapoxetine
4-{4-[4-(hydroxydiphenylmethyl)-1-piperidinyl]-1-butynil}-α,α-dimethyl benzene acetic acid
CAS No: 832088-68-3
For Fexofenadine HCl
Methyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobutanoyl)phenyl)-2-methylpropanoate
CAS No:154477-54-0
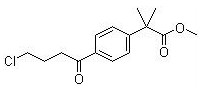
For Fexofenadine HCl
5-Bromo-2-chlorophenyl)(4-ethoxyphenyl)methanone
CAS No 461432-22-4
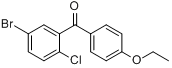
For Dapagliflozin
4-(5-Bromo-2-chlorobenzyl)phenyl ethyl ether
CAS No :461432-23-5
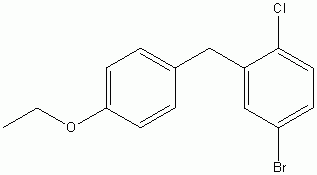
For Dapagliflozin
How to choose the right LIMS--25 function boards, do you have them all?