Enzymes are proteins that catalyze most of the chemical reactions that occur in the body, allowing these reactions to occur at neutral pH and body temperature. Enzymes are not modified or consumed during reactions, thus enabling their reuse in biochemical processes and their detection and study in the field of Clinical Microbiology and Biotechnology. The chemical compound on which the enzyme exerts its catalytic activity is called a substrate. Each specific enzyme binds to its corresponding substrate and modifies it, promoting its transition from a reactive state to a product state. This substrate-enzyme interaction is fundamental for a large number of biological functions and metabolic processes. Enzymes are usually named according to the molecules they interact with – substrates – and their names typically end with the suffix “-aseâ€.  Chromogenic substrates are colourless soluble molecules consisting of a chromophore – a chemical group that, after enzymatic cleavage, releases colour – and a specific enzymatic substrate. They are synthetically produced and are designed to possess a selectivity similar to the natural substrate for the enzyme. These compounds are useful for enzymatic detection, as chromogenic substrates specifically bind with the target enzyme. This reaction allows the enzyme to catalyze the separation of the chromophore group, resulting in an insoluble product with a distinctive colour – releasing the chromophore – that confirms the existence and activity of the enzyme under study. This colour change can be followed spectrophotometrically and is proportional to the proteolytic activity of the enzyme. Chromogenic substrates facilitate the quantitative and qualitative identification of enzymes and proteins in laboratory experiments, thanks to their visible colour change. This chromatic transition, whose intensity can be quantified, allows the precise measurement of the enzymatic or protein target in chromogenic assays. Its use is common in techniques such as Western blot, ELISA, immunohistochemistry, enzymatic assays, and microbial detection in culture media. Common enzymes in chromogenic assays are Alkaline Phosphatase (AP), β-Galactosidase, and Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP). DC Fine Chemicals, an international supplier dedicated to providing high-quality fine chemicals for production, that meet the needs of their customers, presents a new range of chromogenic products:  (Deep Blue) (Blue Green)   (Pink)  (Blackish purple) The substrates Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate disodium (BCIP) and Nitro blue tetrazolium chloride (NBT) are commonly used together as a combination of chromogenic substrates. In experiments using BCIP-NBT, the corresponding enzyme linked to the probe antibody is alkaline phosphatase (AP). BCIP-NBT can be used in Western blot techniques, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and can be added to solid microbiological media to detect AP activity in microbial cultures. The product formed is a dark purple colour that can be easily visible. Figure 1: Chromogenic reaction using BCIP-NBT as substrate. Chromogenic substrates have a wide range of applications, mainly in:  If you are interested in fine chemicals, be sure to visit our website, where you can also find chemical products that suit your business. If you need to know more about our chromogenic substrates or any other product, please contact us:   References:  Article written by Sherry Cacay, Marketing Manager of DC Fine Chemicals
 Discover our Chromogenic Substrates One-click Video Measuring Machine- Vertical
This equipment is widely used in electronic manufacturing, automotive manufacturing, mechanical processing, LCD displays, medical devices, industrial materials, aerospace, precision hardware, green energy, and other small-scale products and components for batch rapid measurement.
Instrument Introduction
Instrument functions One-click Video Measuring Machine- Vertical,One Button Video Measuring Instrument, Fast Vision Measuring Machine, Instrument Vertical Zhejiang dexun instrument technology co., ltd , https://www.dexunmeasuring.comChromogenic Substrates Overview
Enzyme-Substrate Specificity
What are chromogenic substrates?
Clasification
DCFC Code
Substrates
Synonims
CAS
Enzyme
Lapis Substrates
125290
5-Bromo-3-indolyl phosphate disodium salt
Blue-phos
16036-59-2
Alkaline phosphatase
X-Substrates
125030
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-cellobioside
X-Cellobioside
177966-52-8
β-Cellobiosidase
125000
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl caprylate
X-Caprylate
129541-42-0
Esterase
125220
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-α-D-galactopyranoside
X-α-Gal, X-α-D-Galactoside
107021-38-5
α-Galactosidase
124980
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-α-D-glucopyranoside
X-α-Glucoside
108789-36-2
α-Glucosidase
124960
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide
X-N-Acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide; X-Glucosaminide
4264-82-8
N-Acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase
Magenta Substrates (Magenta to Lilac)
125020
5-Bromo-6-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
Magenta-glucoside
93863-89-9
 β-Glucosidase
125010
5-Bromo-6-chloro-3-indolyl-α-D-glucopyranoside
Magenta-α-D-glucoside
878495-64-8
α-Glucosidase
124990
5-Bromo-6-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate disodium salt
Magenta-phos
404366-59-2
Alkaline phosphatase
124970
5-Bromo-6-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside
Magenta-gal
93863-88-8
β-Galactosidase
125240
5-Bromo-6-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-glucuronide, cyclohexylammonium salt
Magenta-GlcA CHA salt, Magenta-gluc CHA salt
144110-43-0
β-Glucuronidase
Salmon Substrates
125260
6-Chloro-3-indolyl-α-D-galactopyranoside
Salmon-α-gal
198402-61-8
α-Galactosidase
103380
6-Chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside
Salmon-gal
138182-21-5
β-Galactosidase
125250
6-Chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
Salmon-glucoside
159954-28-6
β-Glucosidase
125230
6-Chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-glucuronide, cyclohexylammonium salt
Salmon-glcA CHA salt, Salmon-gluc CHA salt
138182-20-4
β-Glucuronidase
Other Chromogenic Substrates
125210
5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate disodium salt
X-Phosphate disodium salt, BCIP
102185-33-1
Alkaline phosphatase, often in conjunction with NBT
125270
Nitro blue tetrazolium
NBT, Nitro BT
298-83-9
Alkaline phosphatase
Use of BCIP-NBT substrates
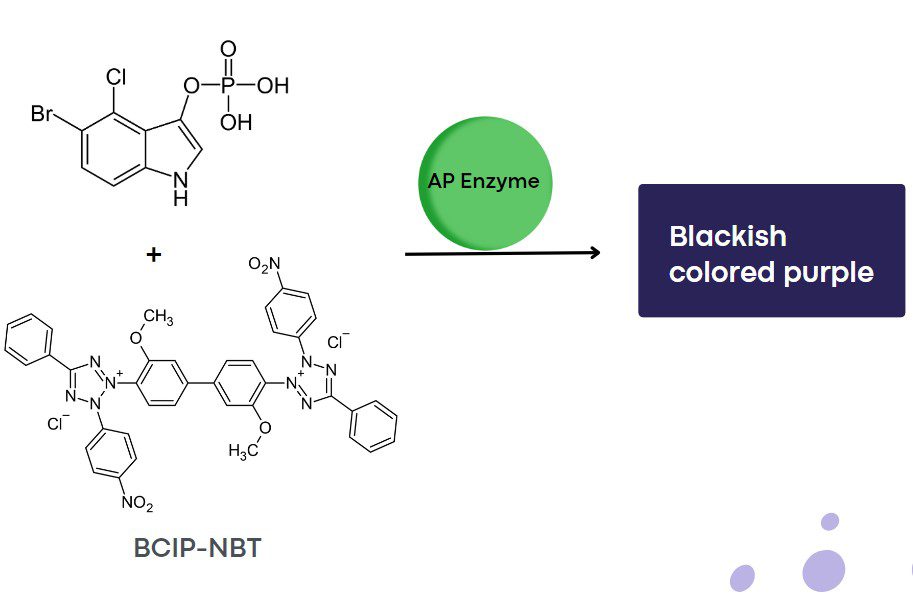
What are their applications?
 Figure 2: Culture Media with chromogenic substrates from CHROMagar™ for detection of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteria (CRE).
Figure 2: Culture Media with chromogenic substrates from CHROMagar™ for detection of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteria (CRE).


1. Ultra large field of view, no distortion, fully automatic, and high-precision.
2. Simply place the workpiece in the effective measurement area and lightly press a button to instantly measure all two-dimensional dimensions.
3. Any workpiece can be placed and multiple measured objects can be recognized simultaneously.
4. Any tedious measurement task becomes incredibly simple.
1. Automatic matching: For the same product, it only needs to be programmed once and automatically matched during measurement.
2. One click calibration: multi angle, full field of view, ensuring measurement accuracy.
3. Measurement function: any two-dimensional point, highest point, line, highest line, circle (center coordinate, radius, diameter, roundness, perimeter, area, maximum radius, minimum radius), arc, rectangle (center coordinate, length, width, perimeter, area), ellipse (center coordinate, major axis, minor axis, perimeter, area), keyway (center coordinate, length, width, perimeter, area), imported CAD contour scanning comparison, contour PV Area comparison, cylinder diameter, sealing ring (radius calculated through perimeter, maximum radius, minimum radius, thickness of sealing ring), measurement results recalculation (maximum, minimum, average, sum), QR code recognition, barcode recognition.
4. Contour scanning: Quickly scan contours and export DXF files.
5. Easy to use: easy to learn, use, and get started.

Chromogenic Substrates Overview
Prev Article
The role of bilirubin conjugate in metabolism