In recent years, with the advancement of the concept of precision medicine, the application of genetic testing technology in commercial or medical science is highly respected. It is like giving a detailed specification to the human body, telling you in detail where you are talented and possible in the future. What disease? A few days ago, the US "New York Times" conducted in-depth research and coverage of the topic, and the problem was not as simple as we thought. At least for the moment, it is a luxury to count on genetic testing to give you a lifetime of talent and health. Genetic testing also needs to be “reworked� According to the New York Times, in a recent study, researchers at Myriad Genetics re-evaluated data from 1.45 million patients who had undergone genetic testing between 2006 and 2016 to view these original reports. Is the result in the truth true? The lab issued a new genetic test report to 60,000 of them, which means that the old results have been completely replaced by new data. But many patients carrying the reclassified mutant gene are still in the dark. Dr. Sharon Plong, clinical genetics expert at Baylor College of Medicine in the United States, said: "This system is still in chaos," she said. "In fact, there is currently no systematic way to tell patients and doctors exactly. The risk of a patient suffering from a disease in the future.†Because some mutations that were previously thought to be harmless may show health hazards in a few years; other mutations that were previously thought to be dangerous may prove to be benign at any time. Simply put, the above report in The New York Times tells us that the genes you tested a few years ago may now have completely turned into another result. Of course, such problems are more likely to affect a small number of patients with a small number of patients, most of them have unusual genetic mutations. More common mutations that cause disease, such as those that predict that you may have breast or colon cancer, have been studied in depth, so their meaning usually does not need to be questioned. I have been widely regarded as a "surprisingly reliable" genetic test. What went wrong? If you want to find out the problem, you need to talk about the mechanism of genetic testing. It is well known that the information carried by DNA strands in human chromosomes determines our physiological structure and behavior. About 1.5% of the code is responsible for describing the composition and structure of all proteins in the human body. Other codes are responsible for describing the construction and life cycle of the human body as a complex organism. But this simple description makes it easy for us to compare the DNA information in a chromosome with a computer program: both are code sequences of long strings of coding elements to illustrate one or more complex tasks. However, this analogy can easily lead to the misconception that the coding on the DNA chain is the same as a computer program, "a piece of coding says one thing", that is, each gene point determines a different physiological or behavioral structure. It is also based on this understanding that we began to try to construct a systematic interpretation of DNA information, namely genetic testing. However, recent studies have shown that these attempts are facing great challenges. The biological mechanism of proteins faces the lack of “singularity†(functionality only) and “uniqueness†(activator only). A simple protein composition, which may be associated with several or even dozens of gene points, changes in one gene point, and it will "catch the whole body". This undoubtedly raises the difficulty of genetic testing by several orders of magnitude. The path of human exploration of genes is longer than expected, and it has caused some phenomenon that genetic testing involving complex pathology will be “reworked†every few years. Don't use it as a "fortune teller" As mentioned above, recent studies have shown that the complexity of DNA coding is not as one-to-one correspondence as computer programs. So far, research on predicting human physiology and even human abilities through gene sequencing should still be in its infancy. Regardless of the commercial organization or the medical institution, what can be done at present is mainly to track and identify genes at a single point. This determines that in the current genetic testing of red fire, some conclusions are reliable, while others are similar to "electronic fortune telling". For example, current technologies have been able to identify genetic errors in genetics and replication by comparing genetics to correspond to diseases caused by specific protein defects. Therefore, genetic testing is used to identify the risk of certain diseases. It is possible. For complex and multifactorial systemic symptoms, prediction by means of gene sequencing has not yet achieved the desired results. We must admit that for most conditions, a stable and reliable correspondence between genes and disorders is very difficult to establish. For another example, since we have been able to track and identify some specific gene loci, we can do it by genetic testing to find out the ancestors of a person. At present, the shortcomings of this technology to be complemented are that the samples are not enough, and only a more general description can be made. However, by measuring a certain "genius gene", it is quite arbitrary to judge how a person's IQ is and how physical fitness is suitable for being a musician or an athlete. Because IQ, physical fitness, music and other qualities involve a rather complicated mechanism. At the protein level, humans have not yet clarified its mechanism, and it is even more impossible to go deep into the genetic level. In addition, the question of what external factors will affect gene expression is still inconclusive in the academic world. A rather interesting but always overlooked fact: two individuals of identical twins have identical chromosomes, but often develop significant differences in personality, abilities, strengths, and preferences during growth, even in almost identical In the culture environment, this difference still occurs frequently. The existence of this phenomenon undoubtedly reminds people that simple genetic determinism is not reliable. All in all, the current research at least shows that there is no "perfect gene" in the world, no people without disease genes. When you are sick, when you are sick, what is sick, how is the disease induced, what kind of talent you have, etc., genetic testing alone cannot be accurately determined. Scientists continue to remind the public that genetic testing has early-warming value for disease, but it cannot be overly deified, and genetic testing should not be regarded as a "fortune-telling artifact." As for what I want to rely on genetic testing to predict what I am "individually talented" in some way, I am afraid it is even more whimsical. If there is any testing agency that says it can do it - it doesn't run, it must be fooling you! (Reporter Wang Wei)
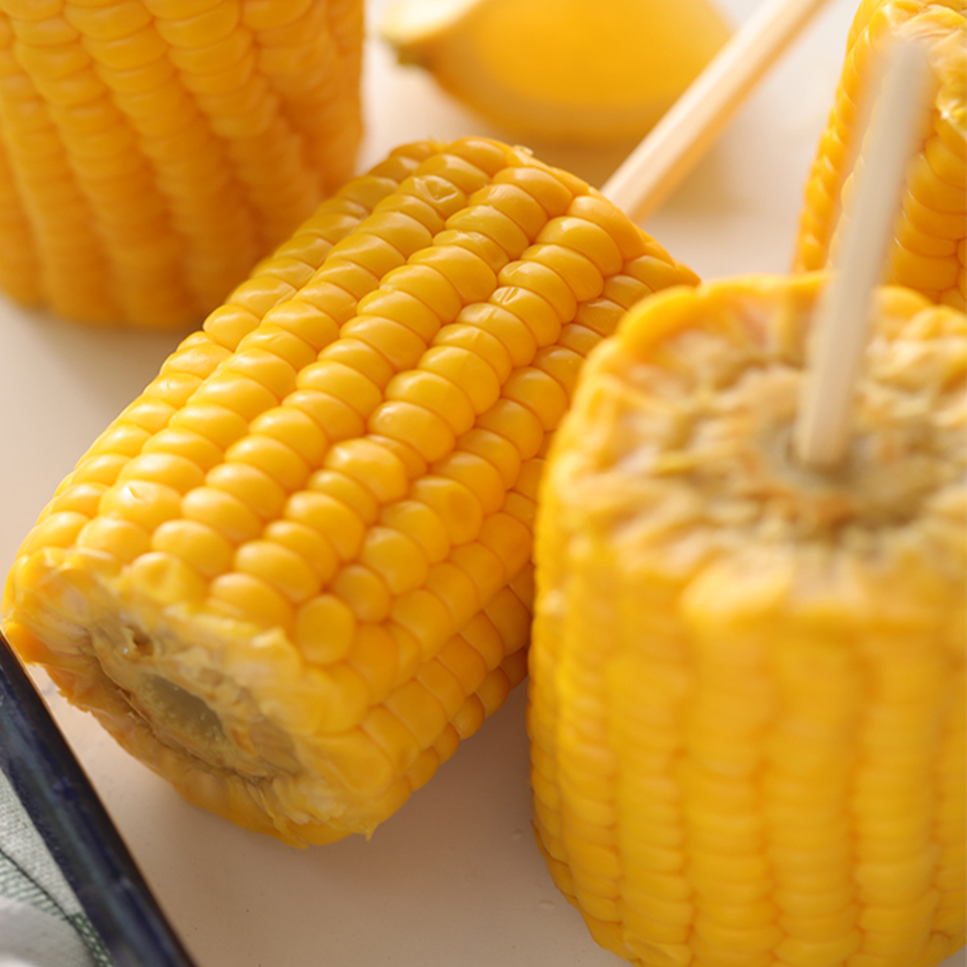
Corn are the expression of some anthocyanins produced by the photosynthesis of grains. Different anthocyanins cause different colors.
If you have any questions, please leave a comment on this website or contact us using email.
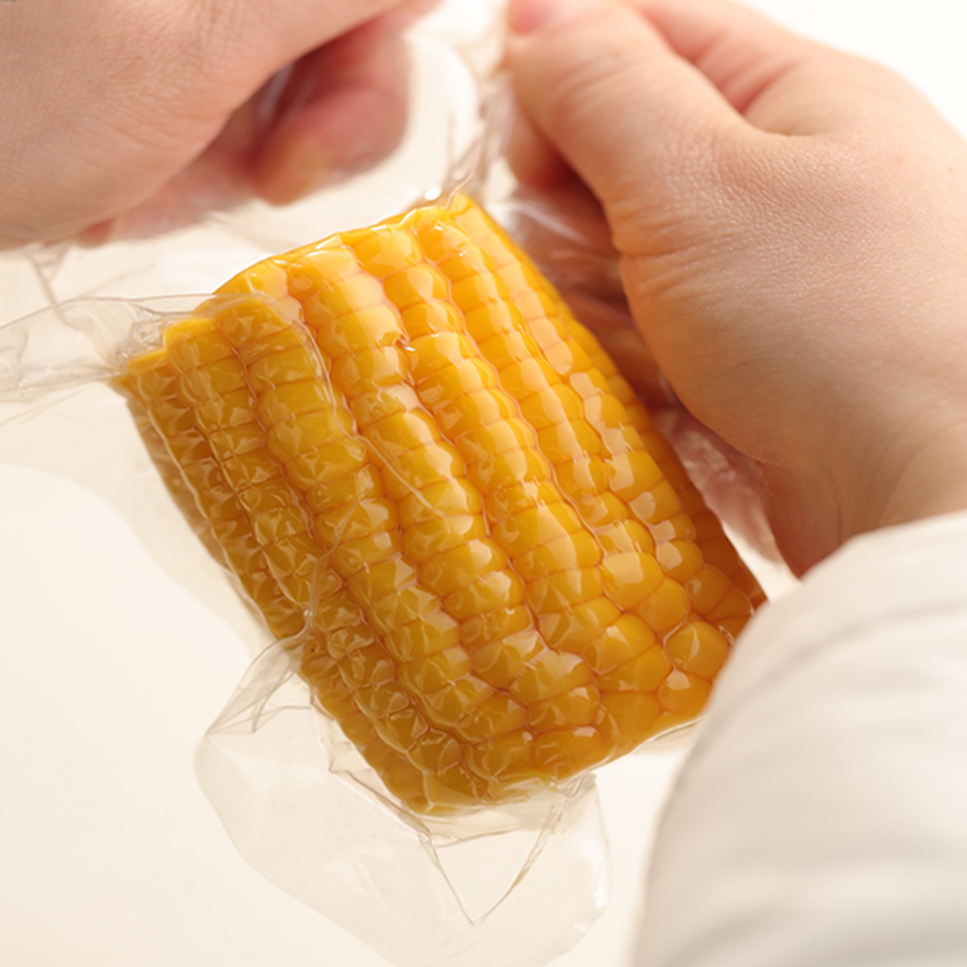
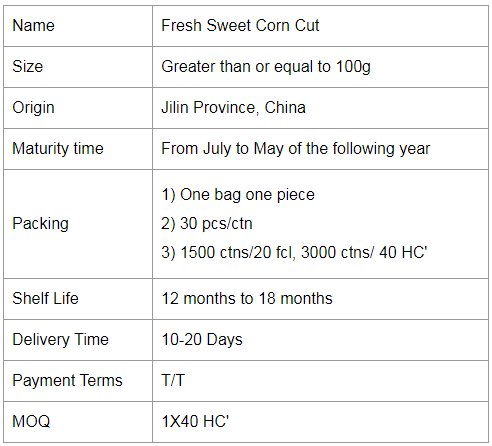
Creamed Corn Cut,Sweet Corn Cut,Cream Sweet Corn Cut,Fruit Corn Cut Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorns.com
There are some benefits of corn: 1. Corn can lower sugar;2. The high content of unsaturated fatty acids in maize is beneficial in preventing atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and other diseases; 3. Corn whiskers have diuretic and hypotensive effects, lowering sugar.


Is genetic testing the god you want?
Next Article
How to trim and reshape elm leaf plum?
Prev Article
Simple identification method of phosphate fertilizer